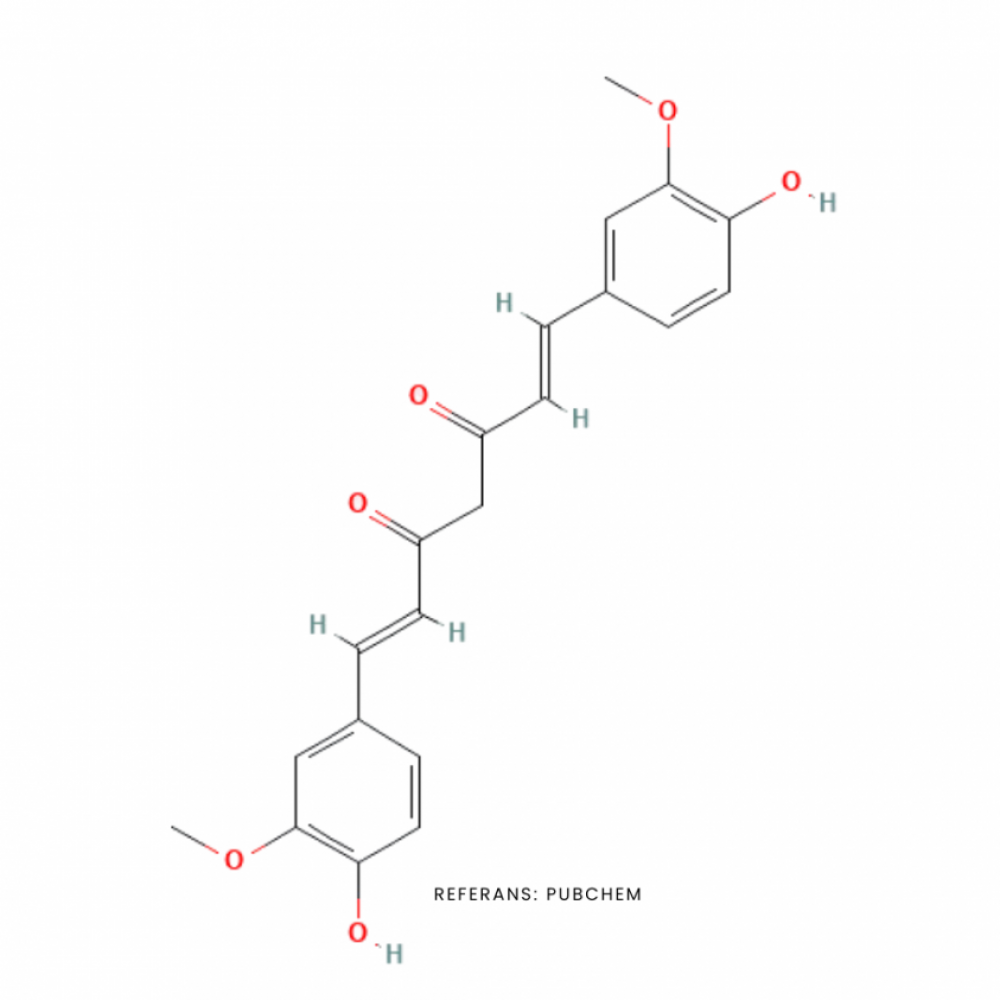
Curcumin is a biologically active yellow polyphenolic compound found in turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) from the ginger family (Zingiberaceae). Curcumin, one of the curcuminoids found in turmeric, is generally considered its most active component.
Molecular Formula: C21H20O6
Molecular Weight: 368.4 g/mol
PubChem CID: 969516
CAS Number: 458-37-7
Synonyms: Turmeric
MeSH Pharmacological Classification:
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal: Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects.
Antineoplastic Agents: Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS
Curcumin acts as a scavenger of oxygen species, such as hydroxyl radical, superoxide anion, and singlet oxygen and inhibit lipid peroxidation as well as peroxide-induced DNA damage. Curcumin mediates potent anti-inflammatory agent and anti-carcinogenic actions via modulating various signalling molecules. It suppresses a number of key elements in cellular signal transduction pathways pertinent to growth, differentiation, and malignant transformation; it was demonstrated _in vitro_ that curcumin inhibits protein kinases, c-Jun/AP-1 activation, prostaglandin biosynthesis, and the activity and expression of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX)-2.