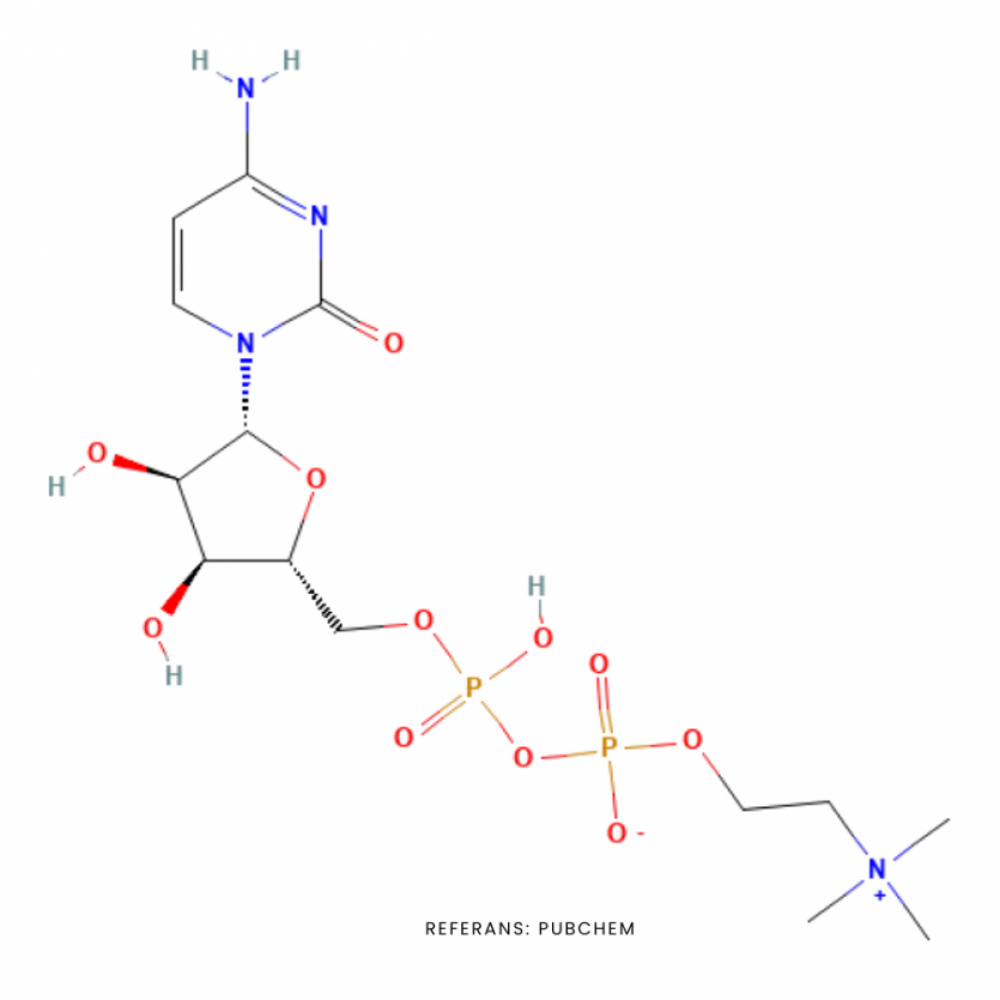
Citicoline (INN), is an intermediate in the generation of phosphatidylcholine from choline, a common biochemical process in cell membranes. Its formal chemical name is Cytidine 5'-diphosphocholine, and it's often used as a dietary supplement. Citicoline is also used as medication in parenteral form. Citicoline (INN), also known as cytidine diphosphate-choline (CDP-Choline) or cytidine 5'-diphosphocholine. Citicoline is naturally occurring in the cells of human and animal tissue, particularly in the brain. It's made up of cytidine and choline connected by a diphosphate bridge. Exogen citicolin is a source of choline and cytidine, which play a role in brain health by stimulating the synthesis of brain phospholipids. This process helps produce more phosphatidylcholine and other important substances, supporting mental health and improving brain performance. Studies have also revealed its benefits for age-related decline in memory and thinking, glaucoma, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, bipolar disorder, depression and many other problems.
Molecular Formula: C14H26N4O11P2
Molecular Weight: 488.32 g/mol
PubChem CID: 13804
CAS Number: 987-78-0
Synonyms: Cytidine diphosphate-choline (CDP-Choline), cytidine 5'-diphosphocholine
MeSH Pharmacological Classification: Nootropic Agents
Drugs used to specifically facilitate learning or memory, particularly to prevent the cognitive deficits associated with dementias. These drugs act by a variety of mechanisms.
ATC Code:
N - Nervous system
N06 - Psychoanaleptics
N06B - Psychostimulants, agents used for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and nootropics
N06BX - Other psychostimulants and nootropics
N06BX06 - Citicoline
Citicoline is a molecule effective on the brain. This mechanism of action can be explained as follows:
• It facilitates the healing of the damaged cell wall.
• Inhibits (blocks) the effect of the phospholipase enzyme.
• It prevents free radical formation and prevents cell death by affecting apoptosis mechanisms.
• It increases dopamine and norepinephrine and contributes to serotonin levels.
• Serves as a precursor to acetylcholine.
• Helps reduce levels of glutamate, a chemical that damages the brain in low oxygen conditions.