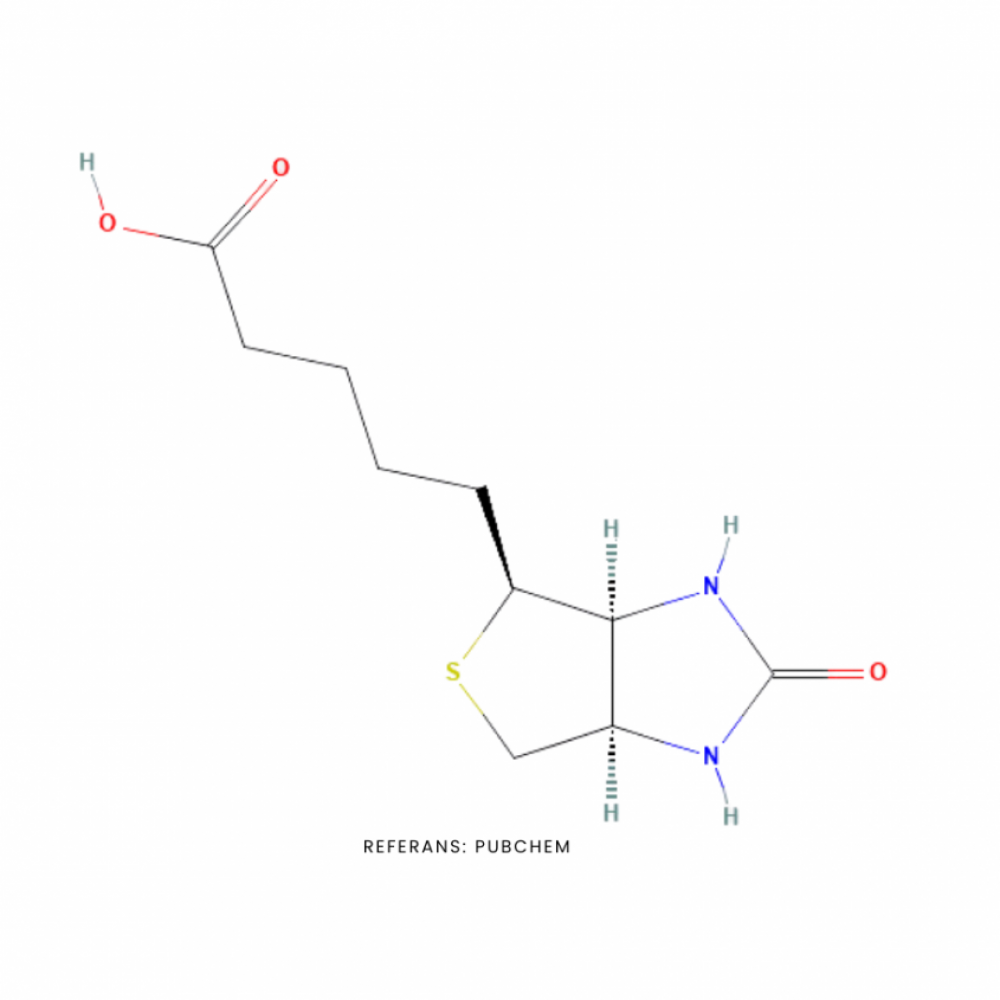
Biotin is a water-soluble B vitamin found naturally in some foods and used as a dietary supplement.
Molecular Formula: C10H16N2O3S
Molecular Weight: 244.31 g/mol
PubChem CID: 171548
CAS Number: 58-85-5
Synonyms: d-biotin, vitamin H
MeSH Pharmacological Classification: A group of water-soluble vitamins, some of which are COENZYMES.
ATC Code:
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A11 - Vitamins
A11H - Other plain vitamin preparations
A11HA - Other plain vitamin preparations
A11HA05 - Biotin
Biotin is a dietary compound important for the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and amino acids. It is especially found in the liver, kidney and muscle. Biotin functions as an essential cofactor for five carboxyls that catalyze steps in glucose and amino acid metabolism. It is also an important factor in histone modifications, gene regulation and cell signaling. Biotin as a dietary supplement has been recognized to be useful in hair and nail problems, in the treatment of host diseases in patients with phenylketonuria, in the treatment of biotinidase deficiency, diabetes, peripheral neuropathy, candida infections and high cholesterol. Additionally, since biotin levels are low in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, supplementation is recommended in these cases.